📼 Build an MCP Server with Java at Devoxx Belgium
Video of my Devoxx deep dive session about how to build an MCP Server with Java.
📼 Build an MCP server with Java at Madrid JUG
I delivered a talk in Spanish about how to build an MCP server using Java frameworks like Micronaut, Spring Boot, and Quarkus at Madrid JUG.
I updated the MCP demos in my GitHub Repository, and the video is available on the Madrid JUG YouTube channel.

StringTemplate
While reading Spring AI in Action, I discovered StringTemplate.
StringTemplate is a Java template engine for generating source code, web pages, emails, or any other formatted text output. StringTemplate is particularly good at code generators, multiple site skins, and internationalization / localization. StringTemplate also powers ANTLR.
I am thinking of adding support for StringTemplate in Micronaut Views.
String template = """
You are a helpful assistant, answering questions about tabletop games.
If you don't know anything about the game or don't know the answer,
say "I don't know".
The game is {game}.
The question is: {question}.""";
String prompt = new ST(template, '{', '}')
.add("game", question.gameTitle())
.add("question", question.question())
.render();
Micronaut NullAway and JSPecify
In this blog post, I show you how to configure a Micronaut 4 application to use JSpecify and NullAway to protect you from NPEs (Null Pointer Exceptions).
NullAway:
NullAway is a tool to help eliminate NullPointerExceptions (NPEs) in your Java code. To use NullAway, first add @Nullable annotations in your code wherever a field, method parameter, or return value may be null. Given these annotations, NullAway performs a series of type-based, local checks to ensure that any pointer that gets dereferenced in your code cannot be null.
JSpecify Dependency
Since Micronaut 4.10, Micronaut BOM contains the JSpecify dependency. Thus, you can add the following dependency to your project without specifying the version:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jspecify</groupId>
<artifactId>jspecify</artifactId>
</dependency>
NullAway with Gradle
GitHub Repository with a Gradle Micronaut Application which uses NullAway
To use NullAway in a Gradle Micronaut Application. You need to add the Gradle error prone plugin and such configuration:
plugins {
...
..
.
id("net.ltgt.errorprone") version "4.3.0"
}
dependencies {
...
..
.
implementation("org.jspecify:jspecify")
errorprone("com.uber.nullaway:nullaway:0.12.12")
errorprone("com.google.errorprone:error_prone_core:2.44.0")
}
tasks.withType<JavaCompile>().configureEach {
options.errorprone {
check("NullAway", net.ltgt.gradle.errorprone.CheckSeverity.ERROR)
option("NullAway:AnnotatedPackages", example.micronaut")
if (name.lowercase().contains("test")) {
disable("NullAway")
}
}
}
check("NullAway", CheckSeverity.ERROR)setsNullAwayissues to the error level.option("NullAway:AnnotatedPackages", “example.micronaut”)tellsNullAwaythat source code in packages under theexample.micronautnamespace should be checked for null dereferences and proper usage of@Nullableannotations, and that class files in these packages should be assumed to have correct usage of@Nullable.- Then, it disables
NullAwayon test code.
These instructions are described in the NullAway README.md file.
NullAway with Maven
GitHub Repository with a Maven Micronaut Application which uses NullAway
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
...
..
.
<properties>
...
..
.
<error-prone.version>2.29.2</error-prone.version>
<nullaway.version>0.12.12</nullaway.version>
</properties>
...
..
.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jspecify</groupId>
<artifactId>jspecify</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
...
..
.
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
...
..
.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<compilerArgs>
<arg>-XDcompilePolicy=simple</arg>
<arg>--should-stop=ifError=FLOW</arg>
<arg>-Xplugin:ErrorProne -Xep:NullAway:ERROR -XepOpt:NullAway:AnnotatedPackages=example.micronaut</arg>
<arg>-Amicronaut.processing.group=mn.maven.jspecify</arg>
<arg>-Amicronaut.processing.module=mn-maven-jspecify</arg>
</compilerArgs>
<annotationProcessorPaths combine.children="append">
<path>
<groupId>com.google.errorprone</groupId>
<artifactId>error_prone_core</artifactId>
<version>${error-prone.version}</version>
</path>
<path>
<groupId>com.uber.nullaway</groupId>
<artifactId>nullaway</artifactId>
<version>${nullaway.version}</version>
</path>
<!-- Existing Micronaut processors -->
...
..
.
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
The above example adds two annotation processors. Error Prone and NullAway.
The previous code sample configures NullAway:
-XepOpt:NullAway:AnnotatedPackagessets the list of packages that should be considered properly annotated according to the NullAway convention-Xep:NullAway:ERRORsets the NullAway check severity to ERROR, which should cause compilation to fail whenNullAwayviolations are found.
As described in the error prone Maven documentation, I added a .mvn/jvmconfig file with the following content:
--add-exports jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.api=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-exports jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.file=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-exports jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.main=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-exports jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.model=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-exports jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.parser=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-exports jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.processing=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-exports jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.tree=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-exports jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.util=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-opens jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.code=ALL-UNNAMED
--add-opens jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.comp=ALL-UNNAMED
A failure looks like:
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[ERROR] Failed to execute goal org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-compiler-plugin:3.14.1:compile (default-compile) on project mn-maven-jspecify: Compilation failure
[ERROR] /Users/sdelamo/github/sdelamo/micronaut-maven-nullaway-demo/src/main/java/example/micronaut/GreetingController.java:[21,39] [NullAway] dereferenced expression greetingService.greet() is @Nullable
[ERROR] (see http://t.uber.com/nullaway )
[ERROR]
[ERROR] -> [Help 1]
[ERROR]
Micronaut Fundamentals
During this year, I recorded Micronaut Fundamentals, a video course available for free on Oracle MyLearn with an OCI Free Learning Subscription.
It is a 7-hour and 37-minute course covering the following topics:
- Introduction to Micronaut
- Micronaut Documentation
- Creating your first Micronaut application
- Using Micronaut in popular IDEs
- Exploring a Micronaut application
- Micronaut Build Plugins
- Micronaut Test
- Micronaut Core Concepts
- Serialization
- Application Events
- Source Code Generation
- Configuration
- Dependency Injection
- HTTP Client
- HTTP Server
- Filters
- Management Endpoints
- Logging
- Validation
- Error formats
- Error handling
- OpenAPI
- Packaging and distribution
- GraalVM Native Image
- Graal Development Kit for Micronaut
Announcement in Oracle Blog.
jCasbin
jCasbin is a powerful and efficient open-source access control library for Java projects. It provides support for enforcing authorization based on various access control models.
System Rules
A collection of JUnit rules for testing code that uses java.lang.System.
Add an MCP Server to GitHub Copilot in IntelliJ IDEA
To register a MCP Server in GitHub Copilot for IntelliJ IDEA, change to Agent model, click the Tools icon and click Add More Tools...
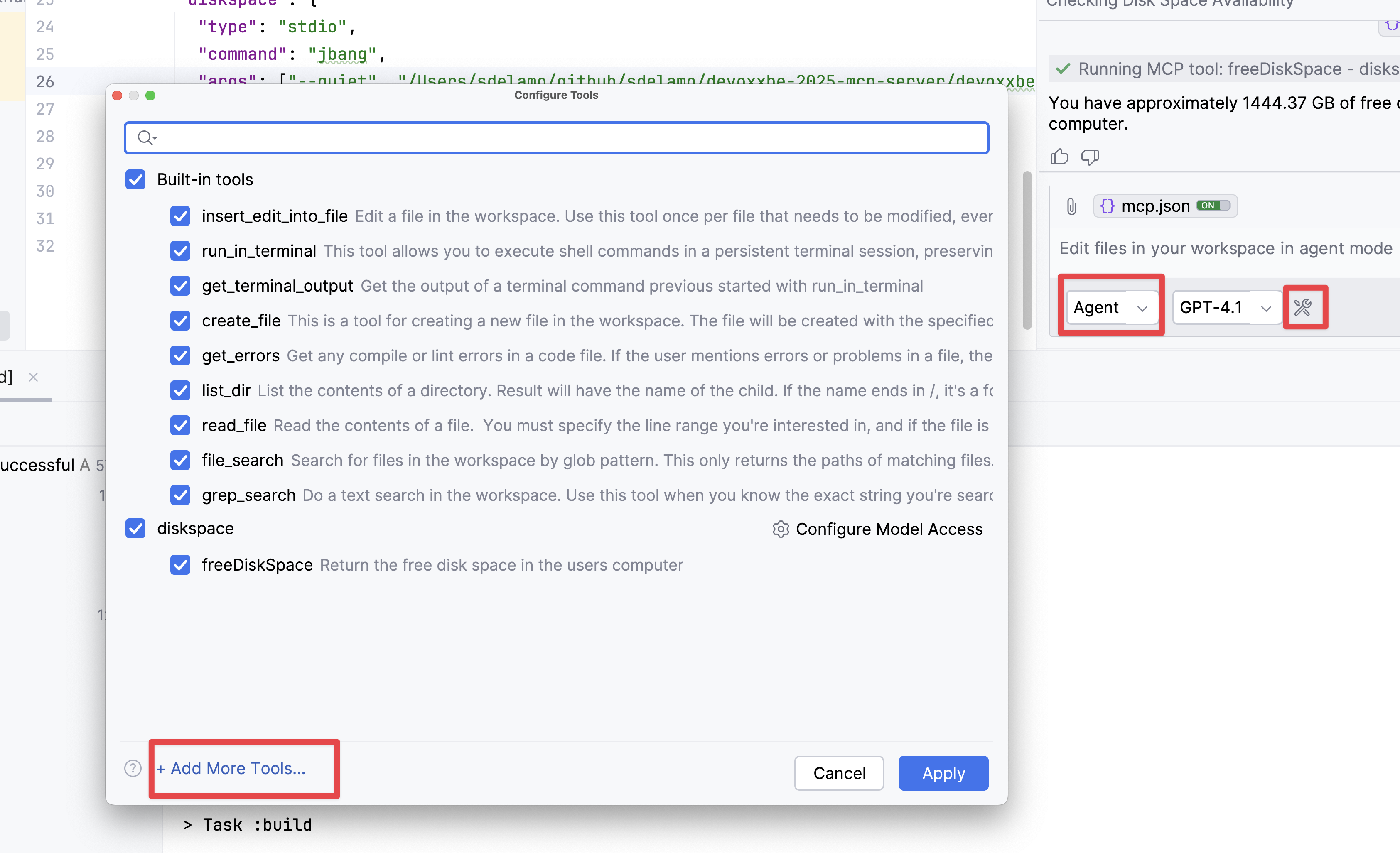
Enter your MCP Server in the mcp.json configuration file. The following example shows an MCP Server packaged as a FAT jar which uses STDIO transport.
{
"servers": {
"diskspace": {
"type": "stdio",
"command": "java",
"args": ["-jar", "/Users/sdelamo/bin/diskspace-0.1-all.jar"]
}
}
}
Add an MCP Server to Claude Desktop
To register a MCP Server in Claude Desktop, click on Settings, click the Developer, and click Edit Config
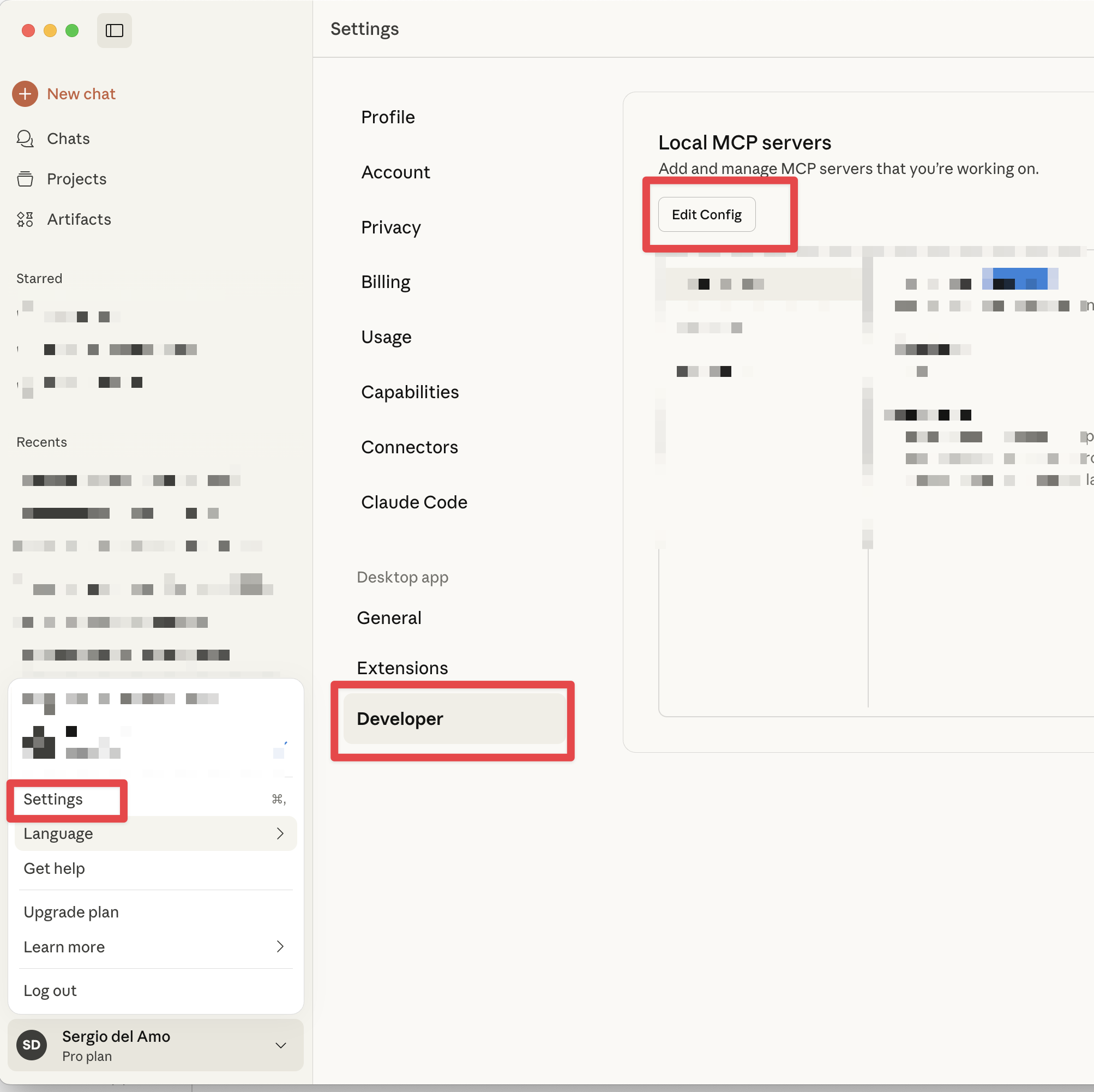
Enter your MCP Server in the claude_desktop_config.json configuration file. The following example shows an MCP Server packaged as a FAT jar which uses STDIO transport.
{
"mcpServers": {
"diskspace": {
"command": "java",
"args": ["-jar", "/Users/sdelamo/bin/diskspace-0.1-all.jar"]
}
}
}
Add an MCP Server to Claude Code
You can connect Claude Code to tools via MCP. You can use the claude mcp add command to add an MCP server.
claude mcp add --transport http micronautfun https://micronaut.fun/mcp
The previous command adds an entry in the mcpServers of the project:
"mcpServers": {
"micronautfun": {
"type": "http",
"url": "https://micronaut.fun/mcp"
}
},
These commands modify the vi $HOME/.claude.json configuration file.
You can list your project MCP servers with the claude mcp list command.
Add an MCP Server to VS Code
To register a MCP Server in VS Code open the command palette with (CMD + Shift + P) and search for "Add MCP"
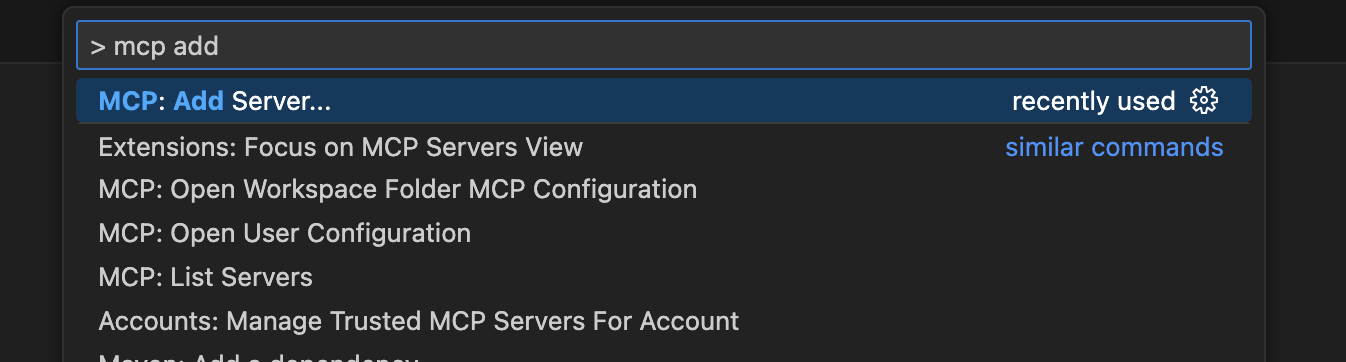
Select your MCP Server transport (STDIO or HTTP)
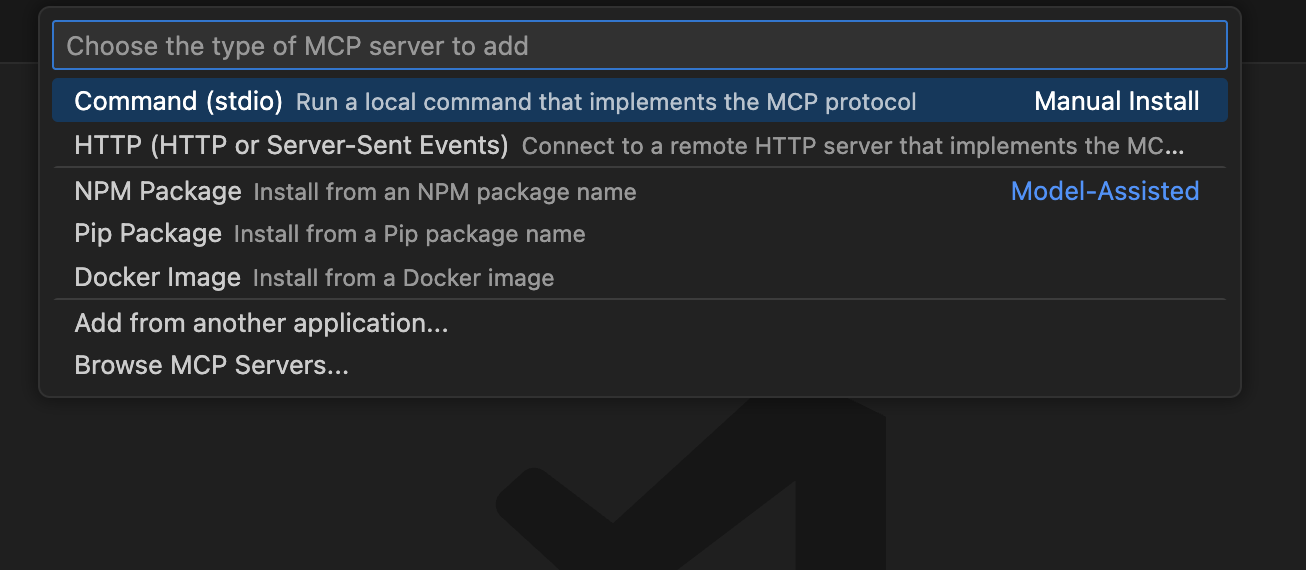
If HTTP, enter your MCP Server URL.
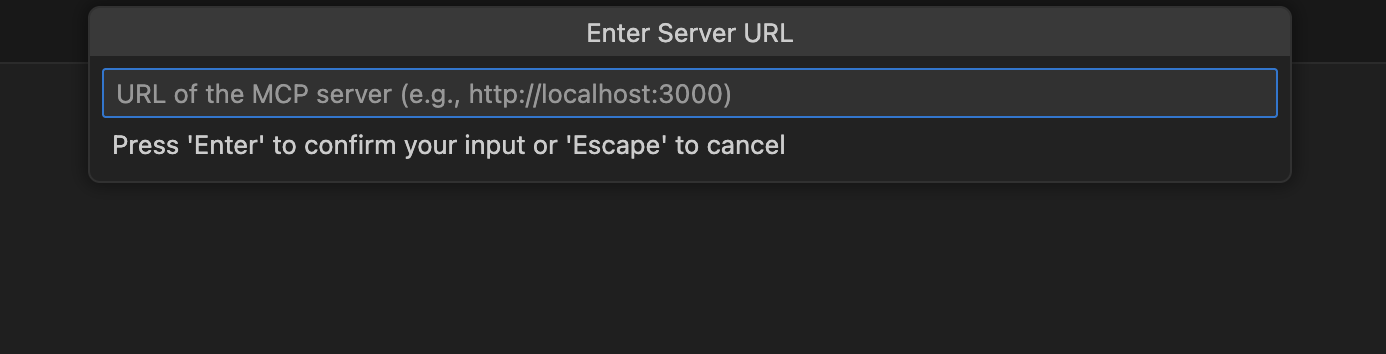
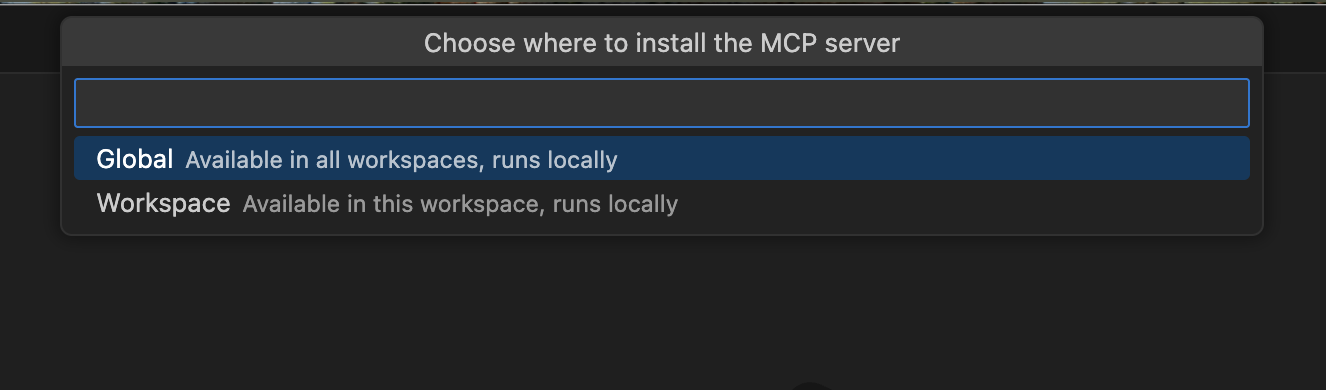
Select whether you want to install the MCP Server globally or for the current workspace only.
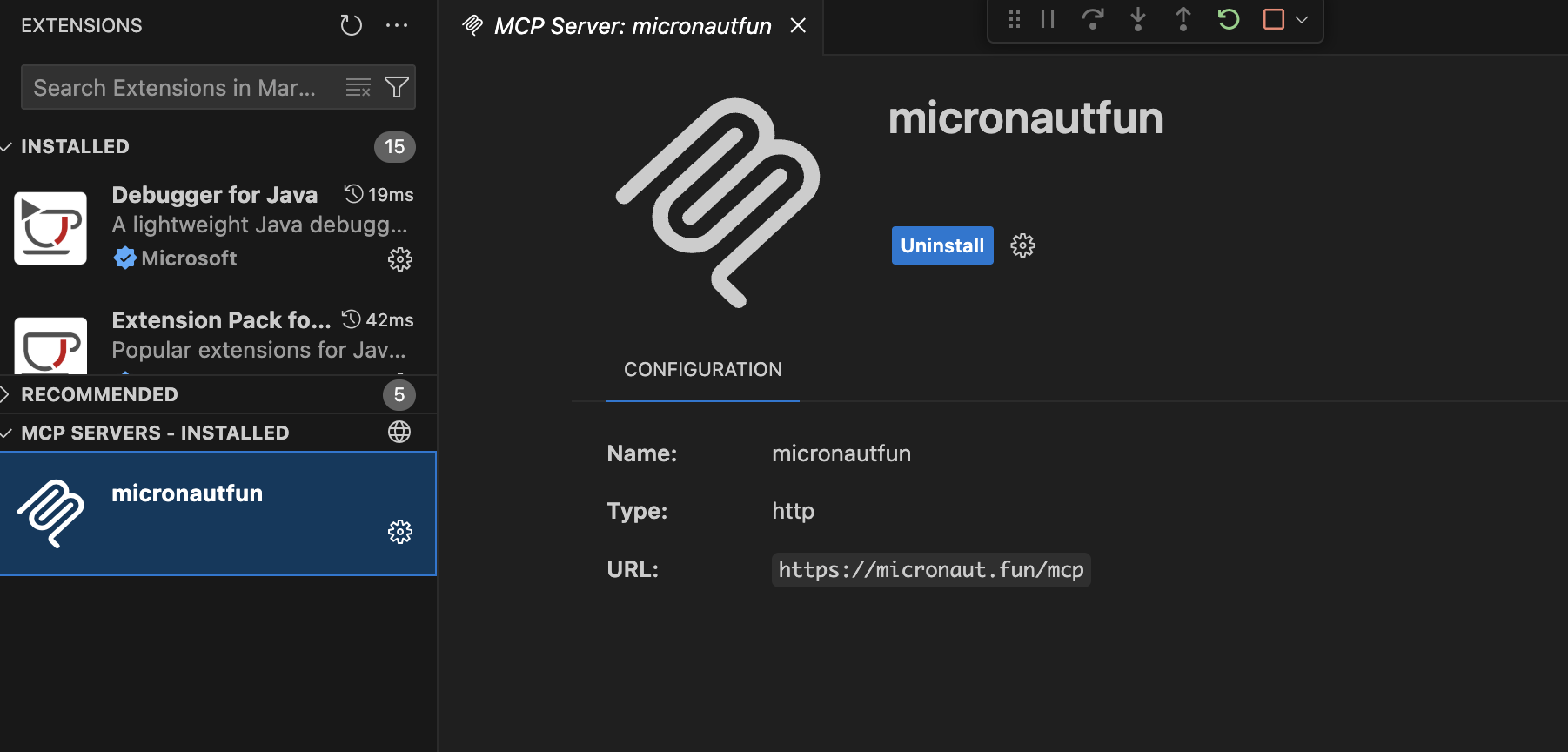
Enter your MCP Server in the mcp.json configuration file.
The following example shows an MCP Server which uses Streamable HTTP transport.
{
"servers": {
"micronautfun": {
"url": "https://micronaut.fun/mcp",
"type": "http"
}
},
"inputs": []
}
You should see your MCP listed as installed.
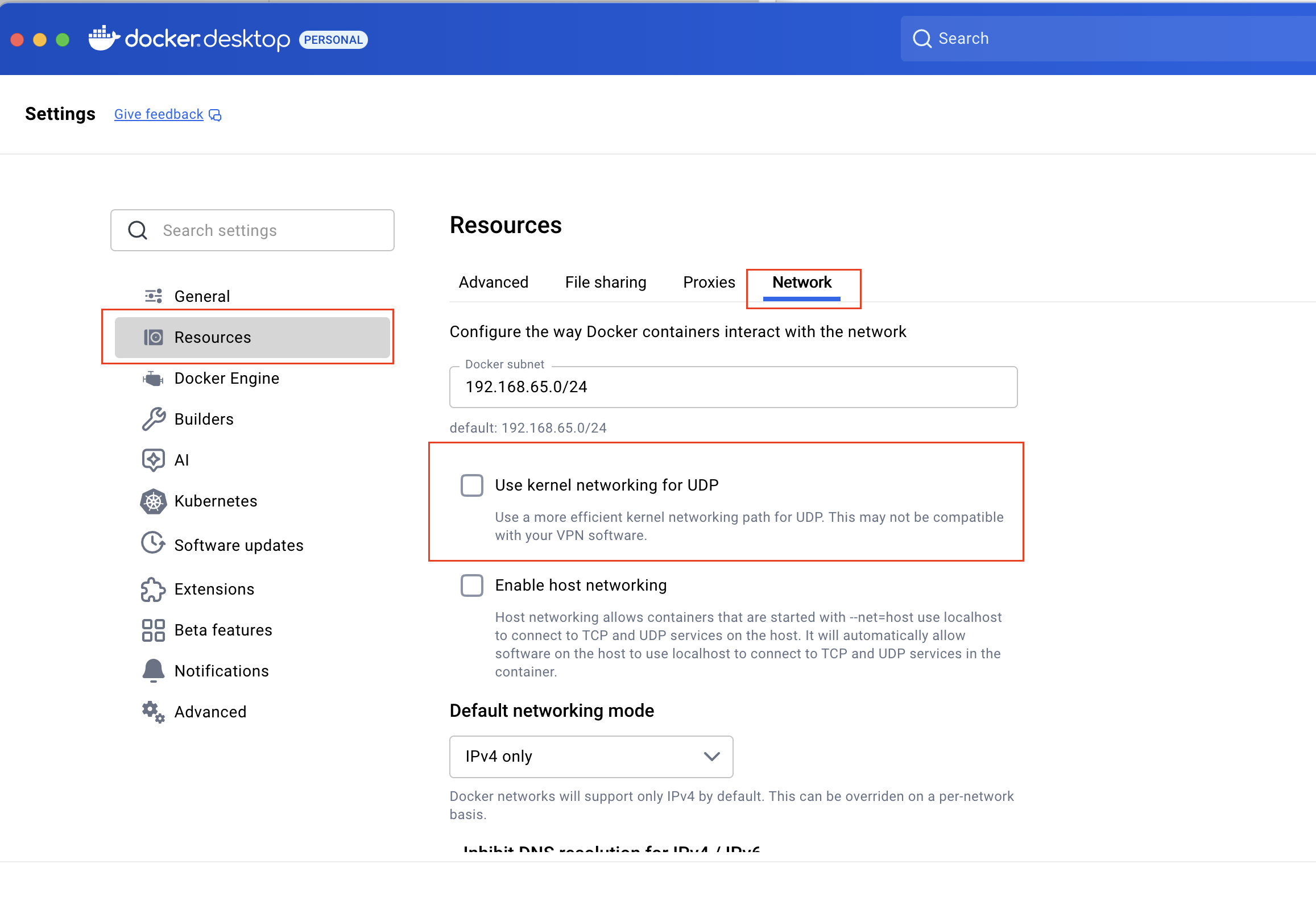
Use Claude Code and Docker Destkop
If you see error messages such as API Error: Connection error while using Claude Code and Docker Desktop, toggling off this setting may help you.
Devoxx Talk - Build an MCP Server with Java
I am excited to be talking at Devoxx Belgium, arguably the most important Java conference in Europe, about how to build an MCP Server with Java.
Moving my Mastodon account to foojay.social
My new handle is @sdelamo@foojay.social.
I followed this video to migrate from jvm.social to foojay.social.
📼 Micronaut Constraints Validation
In this video, I show you how to set up Micronaut Validation to validate the constraints of a Java Record.
📼 Micronaut Development environment
In this video, I show you how to set up a Micronaut Development environment.
📼 Micronaut @EachProperty
In this video, I show you how to use the @EachProperty to load configuration into your Micronaut application.
OSS-Fuzz
OSS-Fuzz aims to make common open source software more secure and stable by combining modern fuzzing techniques with scalable, distributed execution.
Micronaut is using this great initiative by Google.
📼 Micronaut CLI upgrade via SDKMan
In this video, I show how to update to the latest version of the Micronaut CLI with SDKMan
📼 Micronaut Gradle GitHub Actions
In this video, I created a Micronaut application built with Gradle. I pushed it to a GitHub repository and I set up a continuous integration server with GitHub Actions
